Confused about how torque wrenches work?
Perhaps you’re in the market for a torque wrench but unsure whether preset torque wrenches or adjustable torque wrenches are better?
This guide will teach you all you need to know in order to choose, use, and maintain a torque wrench with confidence.

What is a Torque Wrench?
A torque wrench is a tool that makes it possible to tighten nuts and bolts to a predetermined tension, helping you avoid over- or under-tightening.
It’s the perfect tool to use when fastening spark plugs, wheel nuts, and other nuts and bolts that need to be adjusted to a precise tension.
What is Torque?
Torque is the amount of force you need to apply in order to cause rotational movement. When we talk about torque in relation to a torque wrench, we’re referring to the amount of energy needed to turn the nut or bolt.
A good example of torque in action is twisting the lid off a jar or unscrewing a bottle cap. In both scenarios, you are applying torque to complete the action.
Torque is measured in lb-ft (pound-feet) or Nm (Newton-metres), a scale named after Isaac Newton. In the Newton metre measuring system, torque is recorded as the amount of force in relation to the distance required to rotate an object around an axis.
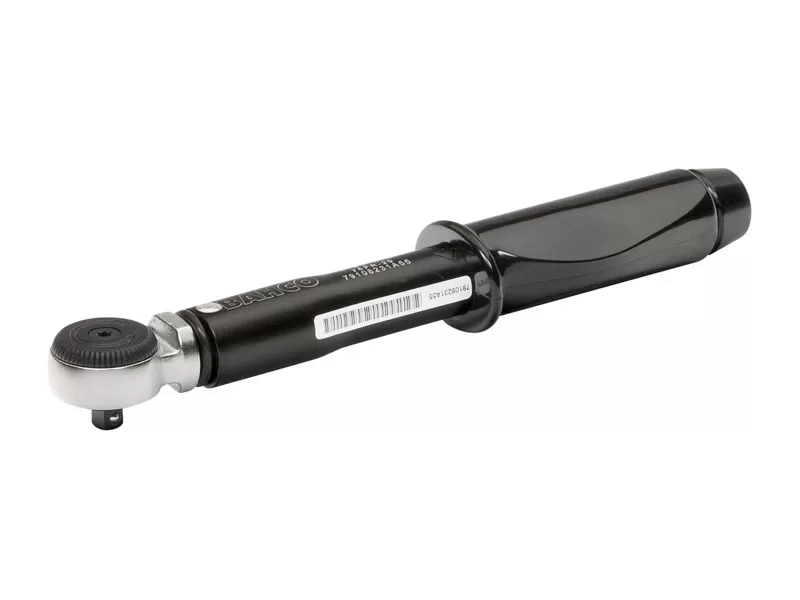

How to Use a Torque Wrench
The steps outlined in this section are specific to using a manually operated torque wrench, such as a click torque wrench (mechanical torque wrench). If using a digital or electronic torque wrench, some of the below steps will be automated.
Adjusting the Wrench
Torque wrenches feature a locking knob at the base of their handle and horizontal measurements around their shaft. To adjust the wrench to the correct torque you must first loosen the locking bolt. This will allow you to twist the wrench handle.
Turning the handle clockwise allows you to increase the torque, while turning it anticlockwise reduces it. Once the measurements align with the torque you need, you simply stop turning. If you need even more precise adjustments, you can then turn the top handle or dial (note, this action differs between torque wrench models, some of which have an independently rotating dial).
Once you’re happy with the adjustments you’ve made, simply screw the locking knob back into place. As you do this, make sure to hold the main portion of the wrench in your non-dominant hand so as not to move the settings you’ve applied.
Tightening Nuts and Bolts
To tighten a nut or a bolt using a torque wrench, first, attach a socket to the head of your wrench. Be sure to select a socket that is the right size for the fastener.
Begin by screwing the nut or bolt in by hand to ensure the fastener is correctly aligned. Once you can no longer turn it by hand, fit the socket of your torque wrench over the fastener and turn the wrench in a clockwise direction. If the wrench slips, choose a smaller socket, more suited to the fastener size.
Depending on the type of torque wrench you’re using, you can either return the wrench to the start position by turning the handle anti-clockwise or your wrench may reposition itself automatically. If your torque wrench doesn’t turn anti-clockwise, you will need to take the wrench off the fastener and reposition it manually.
If you hear a click while turning your wrench clockwise, you feel strong resistance from your wrench, or your wrench stops turning altogether, that’s your sign that the fastener has reached its required tightness and you need to stop turning.
How to Maintain and Store Your Torque Wrenches?
Some handy tips for maintaining and storing your torque wrenches include:
Returning the wrench dial back to 0 between uses.
This will help to maintain the wrench’s calibration. You should also get your wrench recalibrated at least every 5,000 clicks. Recalibrating torque wrenches is vital for maintaining their integrity.
Cleaning the fastener before working with it.
Another key way to extend the life of your toque wrench is by using a rag or wire brush to remove grime or rust from your fasteners before tightening them. Over time, these materials can build up inside the socket, affecting performance.
Types of Torque Wrenches
1. Mechanical (Click Torque Wrenches)
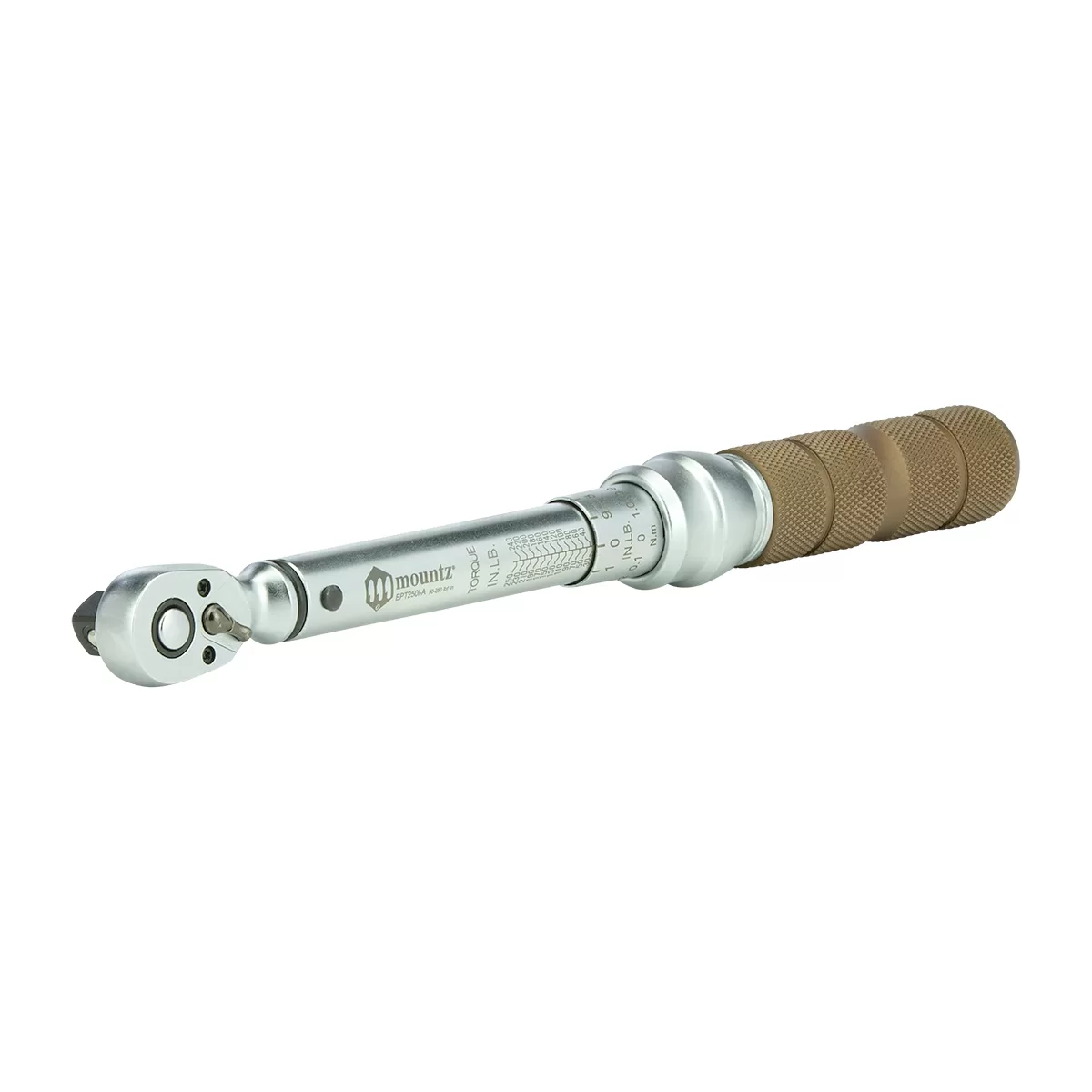

Mechanical torque wrenches need to be adjusted manually with each use (in the way we described earlier in this guide).
This type of torque wrench is also commonly called a click torque wrench, owing to the distinctive click sound the wrench makes when it reaches its pre-programmed torque.
2. Electronic (Digital Torque Wrenches)
An electronic or digital torque wrench is fitted with a torque sensor and a display screen. It can automatically measure torque and gives you the ability to save previously used settings to allow you to easily program the wrench to the required torque each time.
Although more expensive than mechanical torque wrenches, electronic torque wrenches have less margin for error. Some models even allow you to upload data to an external device.

3. Dial Torque Wrenches

A dial torque wrench measures torque with the aid of a dial gauge. It has a reputation for accuracy and is widely used in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
It’s also an incredibly easy torque wrench to use although it’s larger than other torque wrench types, so not great for tight-fitting spaces.
4. Beam Torque Wrenches
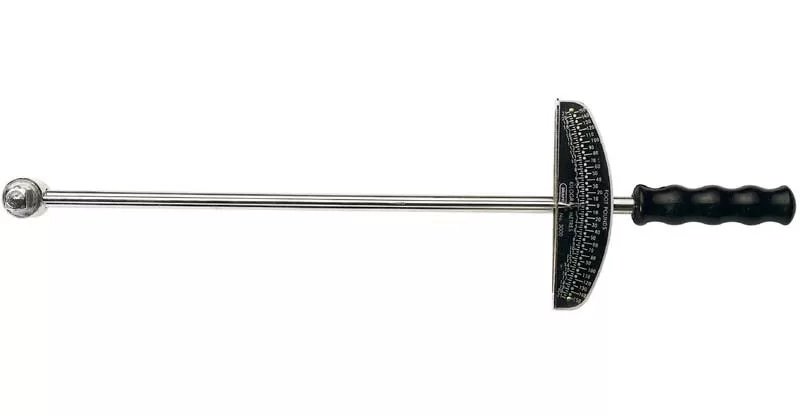
A beam torque wrench is a simple to use torque wrench that features a sliding scale within the handle and a needle that lets you know when the correct torque is applied. As the wrench handle is pulled, the steel beam deflects, and a reading is taken.
Although not as sophisticated as electronic torque wrenches, beam wrenches offer good durability and are well utilised among mechanics.

5. Hydraulic Torque Wrenches
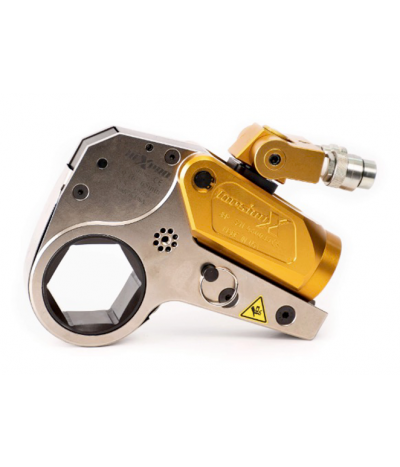

Hydraulic torque wrenches work by converting hydraulic pressure into torque. They feature an internal piston that, when advanced, causes the socket to rotate around the fastener.
Hydraulic torque wrenches are powered by hydraulic oil and should not be operated by anyone unfamiliar with the safe handling of hydraulic equipment.
How Much Torque to Use on Wheel Nuts?

Knowing how much torque to apply to wheel nut sockets is the key to ensuring a vehicle is road-safe. Too loose, and the wheel nut could come off while the car is speeding down the motorway. Too tight, and you risk shearing the nut or damaging the wheel.
The torque value of each car is specified within its handbook, but it should fall somewhere between 110 and 123 Newton meters.
How Much Torque to Use on Spark Plugs?
How much torque you apply to spark plugs can impact the engine’s safety and performance. While too much torque can cause the spark plug to overheat, too little torque can result in cracks in the threads.
Like wheel nuts, the level of torque you need to apply can be found in the vehicle manufacturer’s guidelines. This is usually anywhere between 8 and 40nm.

Torque Wrench Calibration

Torque wrenches need to be routinely calibrated in order to maintain accurate readings.
You should ensure your wrench has been calibrated prior to its first use and aim to have it professionally recalibrated either once a year or every 5000 clicks – whichever occurs first.
Browse our selection of torque calibrating equipment, including sensors, multipliers, transformers, torque analysers and more.
Which are the Best Torque Wrenches to Use?
To view and compare a wide selection of high-performance torque wrenches from trusted tool brands, click below to view the full torque wrench product range.